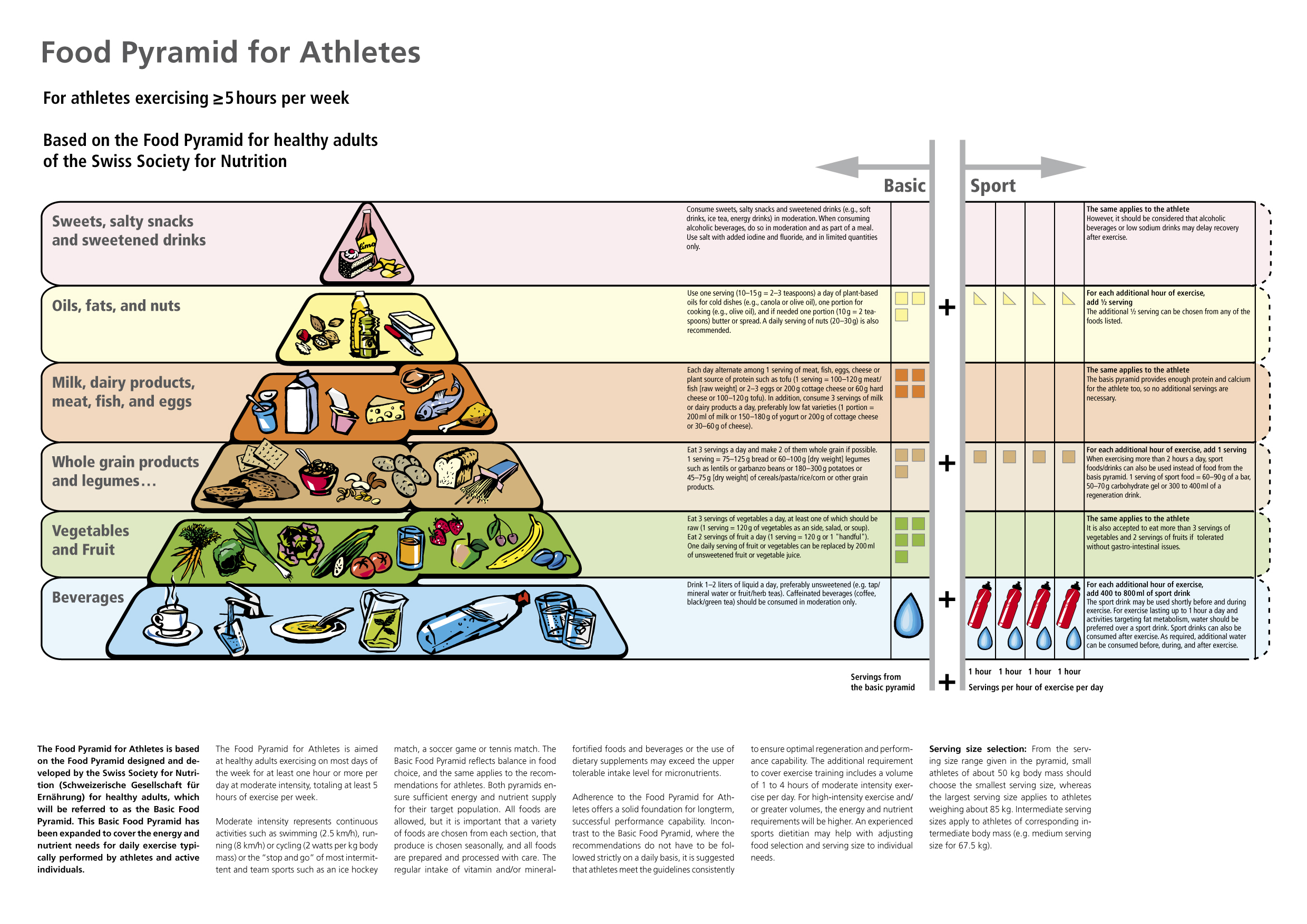
Food Pyramid for Athletes
For athletes exercising > 5 hours per week
Based on the Food Pyramid for healthy adults
of the Swiss Society for Nutrition
|
Basic& | Sport |
| Sweet, salty snacks and sweet- ened drinks |
Consume sweets, salty snacks and sweetened drinks(e.g., soft drinks, ice tea, energy drinks) in moderation. When consuming alcoholic beverages, do so in moderation ans as part of a meal. USe salt with added iodine and fluoride, and in limited quantities only. | The same applies to the athlete however, it should be considered that alcoholic beverages or low sodium drinks may delay recovery after exercise. |
| oils, Fats, and nuts |
Use one serving (10-15g = 2-3 teaspoons) a day of plant-based oils for cold dishes(e.g., olive oil), and if needed one portion (10g = 2 teaspoons) butter or spread. A daily serving of nuts(20-30g)is also recommended. | For each additional hour of exercise, add 1/2 serving The additional 1/2 serving can be chosen from any of the foods listed. |
| Milk, dairy products, meat, fish, and eggs | Each day alternate among 1 serving of meat, fish, eggs, cheese or plant source of protein such as tofu (1 serving = 100-120g meat/fish [raw weight] or 2-3 eggs or 200 g cottage cheese or 60g hard cheese or 100-120g tofu). In addition, consume 3 servings of milk or dairy products a day,preferably low fat varieties (1 portion= 200 ml of milk or 150-180g of yogurt or 200g of cottage cheese or 30-60g of cheese). | The same applies to the athlete The basis pyramid provides enough protein and calcium for the athlete too, so on additional servings are necessary. |
| Whole grain products and legumes… | Eat 3 servings a day and male 2 of them whole grain if possible. 1 serving = 75-125 g bread or 60-100g(dry weight)legumes such as lentils or garbanzo beans or 180-300g potatoes or 45-75g(dry weight)of cereals/pasta/rice/corn or other grain products. | For each additional hour of exercise,add 1 serving When exercising more than 2 hours a day, sport foods/drinks can also be used instead of food from the basis pyramid. 1 serving of sport food = 60-90g of a bar, 50-70g carbohydrate gel or 300 to 400 ml of a regeneration drink. |
| Vegetables and Fruit | Eat 3 servings of vegetables a day, at least one of which should be raw (1 serving = 75-120g of vegetables as an side, salad, or soup). Eat 2 servings of fruit a day (1 serving = 120g or 1 “handful”).One daily serving of fruit or vegetables can be replaced by 200ml of unsweetened fruit or vegetable juice. | The same applies to the athlete It is also accepted to eat more than 3 servings of vegetables and 2 servings of fruits if tolerated without gastro-intestinal issues. |
| Beverages | Drink 1-2 liters of liquid a day, preferably unsweetened(e.g. tap/ mineral water or fruit/herb teas).Caffeinated beverages(cofee, black/green tea) should be consumed in moderation only. | for each additional hour of excercise, add 400 to 800 ml of sport drink The sport drink may be used shortly before and during exercise. For exercise lasting up to 1 hour a day and activities targeting fat metabolism, water should be preferred over a sport drink. Sport drinks can also be consumed after exercise. As required, additional water can be consumed before, during, and after exercise. |
Servings from the basic pyramid + 1hour 1hour 1hour 1hour Servings per hour of exercise per day
| The Food Pyramid for Athletes is based on the Food Pyramid designed and devel- oped by the Swiss Society for Nutrition (Schweizerische Gesellschaft fur Ernshrung) for healthy adults, which wii be referred to as the Basic Food Pyramid. This Basic Food Pyramid has been expanded to cover the energy and nutrient needs for daily exercise typical- lly performed by athletes and active individuals. | The Food Pyramid for Athletes is aimed at healthy adults exercising on most days of the week for at least one hour or more per day at moderate intensity, totaling at least 5 hours of exercise per week. | Moderate intensity represents continuous activities such as swimming (2.5 km/h), running (8km/h) or cycling (2 watts per kg body mass) or the “stop and go” of most intermittent and team sports such as an ice hockey | match, a soccer game or tennis match. The Basic Food Pyramid reflects balance in food choice, and the same applies to the recommendations for athletes. Both pyr- amids ensure sufficient energy and nutrient supply for their target population. All foods are allowed, but it is important that a variety of foods are chosen from each section, that produce is chosen seasonally, and all foods are prepared and processed with care. The regular intake of vitamin and/or mineral fortified foods and beverages or thr use of dietary supplements may exceed the upper tolerable intake level for micronutrients. | Asdherence to the Food Pyramid for Athletes offers a solid foundation for longterm, successful performance capability. In contrast to the Basic Food Pyramid, where the recommendations do not have to be followed strictly on a daily basis, it is suggested that athletes meet the guidelines consistently to ensure optimal regeneration and performance capability. The additional requirement to cover exercise training includes a volume of 1 to 4 hours of moderate intensity exercise per day. For high-intensity exercise and/or greater volumes, the energy and nutrient requirements will be higher. An experienced sports dietitian may help with adjusting food selection and serving size to individual needs. | Serving size selection From the serving size range given in the pyramid, small athletes of about 50kg body mass should choose the smallest serving size, whereas the largest serving size applies to athletes weighing about 85kg. Intermediate serving sizes apply to athletes of corresponding intermediate body mass (e.g. medium serving size for 67.5kg).
|